In the previous article, we introduced the preparation work before CNC machining. Today we introduce CNC machine workflow.
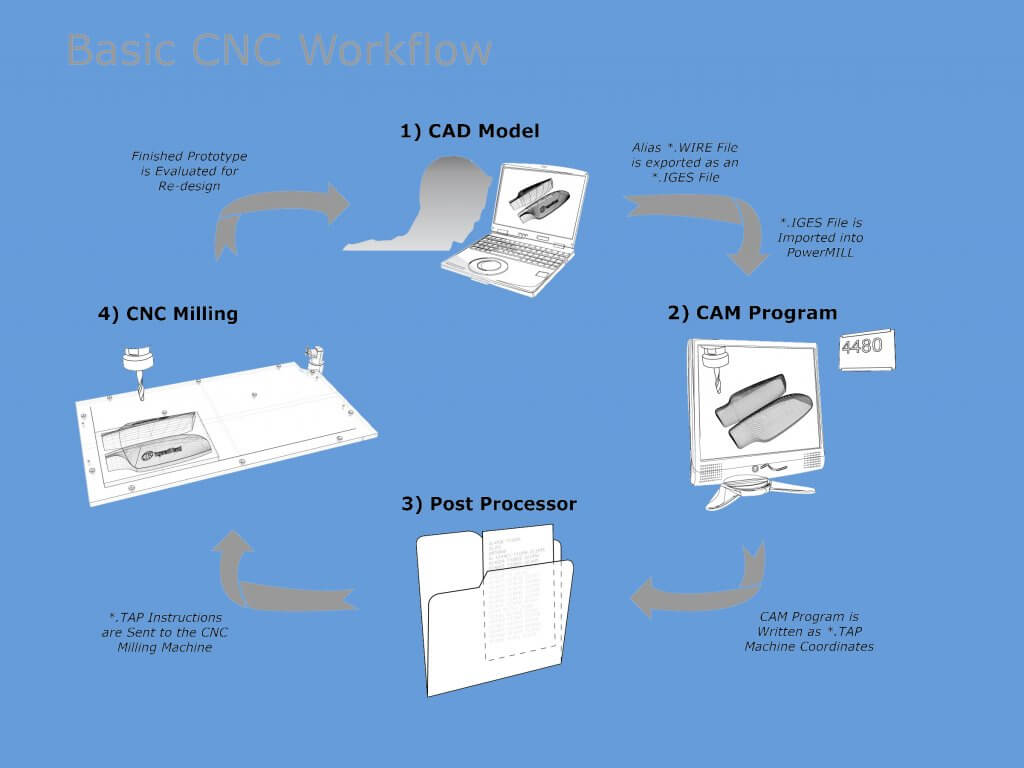
Once the drawing and program reach the machine shop, it is up to the CNC operator to continue with actual production. Production cannot start right away, and certain workflow is followed at the machine as well:
- Evaluate the part program
- Check supplied material
- Prepare the required tools
- Setup and register tools
- Setup part in a fixture
- Load program
- Set various offsets
- Run first part
- Optimize program if necessary n Run production
- Inspect frequently
Evaluate the part CNC program
Evaluating a part CNC program serves the purpose of knowing what it will do and how it will do it. The careful evaluation provides means of organizing the part setup, too1 preparation, and relates activities in an efficient manner. Program evaluation is typically combined with the drawing and material provided.
Check supplied material
Ideally, any material used for CNC work should be qualified as acceptable. Qualified material guarantees consistency in size, shape and condition from one blank piece to another. Unfortunately, this ‘ideal’ condition does not always exist, for different reasons.
A prudent CNC programmer or operator will make a check of at least a sample of the material delivered, and identify the differences if any. Always watch for material inconsistency, not only in size but also in shape and type. Harder material requires different cutting conditions than softer material. Such a situation is common when getting material for the same part from two different suppliers.
Prepare required CNC tools
CNC Tooling generally refers to cutting tools. For CNC machines, cutting tools have two parts – the holder and the cutting tool itself. The tool holder is the part of the assembly that allows the cutting tool to be mounted in the spindle (CNC milling machine) or in the turret (turning center).
Tool holders are standard, and from the setup point of view, the taper that is to be located in the spindle should always be clean. The same applies to the internal area of the spindle, where the holder will be located.

Setup and register CNC tools
Setting up any CNC machine is a multi-step process. Some of these steps have to be performed in a particular order, others have a certain degree of flexibility. Most of the steps are common to all CNC machines, others may vary from one machine manufacturer to another. The first step is the selection of tools. Tools should always be set using an external tool fixture, never in the machine spindle. Use tools that are sharp, preferably new or at least lightly used. If possible, keep frequently used tools in the magazine all the time. This may require cooperation with the programmer, but shortens the unproductive setup time, often significantly.
Setup part in a fixture
CNC machine fixturing is part of work holding. This is the engineering area that studies and develops the most suitable methods of holding a part for safe and consistent machining. The main purpose of a fixture is to safely hold all parts of the batch in a fixed location.
Load CNC program
A part program is typically developed off-machine, either manually or with the assistance of computer software. In order to use such a program, it has been made available to the CNC system. There are two methods to achieve this objective:
- Load the program to the control system
- Run the program from a remote computer
The very early method was to use paper tape for running the program, but this method is now considered obsolete. Loading the completed program to the system memory can be done via the control panel keyboard or via a cable from a remote computer. Both methods will result in the program loaded into the CNC memory. Once the program is loaded, it will run in the memory mode. Programs stored in the memory can also be edited there. Keep in mind that the control system memory has limited capacity and is not designed to store all your programs. Viewing an appropriate screen will show the remaining capacity.
Set various offsets
Offsets are adjustments between fixed positions and actual positions. Although offsets can be set through the program, they are normally set at the control by the CNC operator. The reason why a program cannot be used for all offset setup is simple – the programmer has no way of knowing what the dimensions will be during actual part setup. It is quite normal to have different offsets the next time the same part is machined. There are three groups of offsets (adjustments) available:
- Work offset
- Tool length offset
- Cutter radius offset
It is the are of offsets that the operator’s skills are most required.
Run first part
A lot can be said about running the first part of a given batch. When a certain job is assigned to the CNC machine, production people in the company decide (among other things) on the required output – the number of parts to be machined together in one setup. This number is often called the ‘run’, the ‘order’, the ‘batch’, and may even include some unique local terms as well.
Optimize program if necessary
During the first part run, or even during the run of the next few parts, some program adjustments may be necessary – they generally belong to the features of the program that can be easily edited, such as spindle speeds, cutting, clearances, etc. program optimization make the current program run more efficiently within the given setup.
Run production
When the optimization process is completed, the production run is more than just loading, running, and unloading parts. The operator has to monitor the progress, check dimensions, check tools, replace tools if necessary, adjust offsets, watch the coolant, deburr parts, and do many other tasks.
Inspect frequently
Inspecting a finished part is one of the standard manufacturing processes. Depending on the job, not every part in the batch has been to be inspected, but a certain number of parts in any batch are inspected as a norm. CNC operator may be called upon part inspection as part of everyday duties, or a QI (Quality Improvement) department may be responsible.
In all stages of the machining process, safety should always be paramount.





